13. How to Use Microsoft HyperTerminal to Send AT Commands to a Mobile Phone or GSM/GPRS Modem?
13.1. What is Microsoft HyperTerminal?
Microsoft HyperTerminal is a small program that comes with Microsoft Windows. You can use it to send AT commands to your mobile phone or GSM/GPRS modem. It can be found at Start -> Programs -> Accessories -> Communications -> HyperTerminal. If you cannot find it and you are using Windows 98, then probably you have not installed it. You can go to Control Panel -> Add/Remove Programs -> Windows Setup tab -> Communications list box item -> Details button to install MS HyperTerminal.
Before you start programming your SMS application, you may want to check if your mobile phone, GSM/GPRS modem and SIM card are working properly first. The MS HyperTerminal is a handy tool when it comes to testing your GSM devices. It is a good idea to test your GSM devices beforehand. When a problem occurs, sometimes it is difficult to tell what causes the problem. The cause can be your program, the GSM device or the SIM card. If you test your GSM device and SIM card with MS HyperTerminal and they operate properly, then it is very likely that the problem is caused by your program.
For Linux users, minicom can be used instead of HyperTerminal.
13.2. The Procedure for Sending AT Commands to a Mobile Phone or GSM/GPRS Modem Using MS HyperTerminal
To use MS HyperTerminal to send AT commands to your mobile phone or GSM/GPRS modem, you can follow the procedure below:
Put a valid SIM card into the mobile phone or GSM/GPRS modem. You can obtain a SIM card by subscribing to the GSM service of a wireless network operator.
Connect your mobile phone or GSM/GPRS modem to a computer and set up the corresponding wireless modem driver. You should find the wireless modem driver in the CD or disk that was provided by the manufacturer. If the manufacturer does not provide such CD or disk with your mobile phone or GSM/GPRS modem, you can go to the manufacturer's web site and see whether the wireless modem driver can be downloaded there. If the wireless modem driver cannot be found on the web site, you can still use Windows' standard modem driver.
Run MS HyperTerminal by selecting Start -> Programs -> Accessories -> Communications -> HyperTerminal.
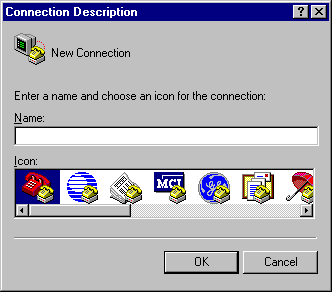
In the Connection Description dialog box, enter a name and choose an icon you like for the connection. Then click the OK button.
|
Figure 5. The screenshot of MS HyperTerminal's Connection Description dialog box in Windows 98. |
|
|
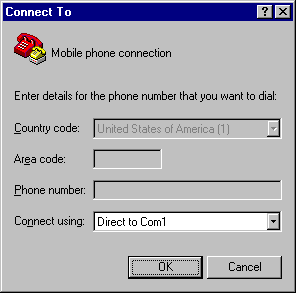
In the Connect To dialog box, choose the COM port that your mobile phone or GSM/GPRS modem is connecting to in the Connect using combo box. For example, choose COM1 if your mobile phone or GSM/GPRS modem is connecting to the COM1 port. Then click the OK button.
(Sometimes there will have more than one COM port in the Connect using combo box. To know which COM port is used by your mobile phone or GSM/GPRS modem, follow the procedure below:
In Windows 98:
Go to Control Panel -> Modem. Then click the Diagnostics tab. In the list box, you can see which COM port the mobile phone or GSM/GPRS modem is connected to.
In Windows 2000 and Windows XP:
Go to Control Panel -> Phone and Modem Options. Then click the Modems tab. In the list box, you can see which COM port the mobile phone or GSM/GPRS modem is connected to.)
|
Figure 6. The screenshot of MS HyperTerminal's Connect To dialog box in Windows 98. |
|
|
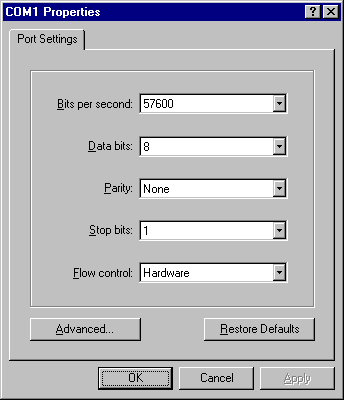
The Properties dialog box comes out. Enter the correct port settings for your mobile phone or GSM/GPRS modem. Then click the OK button.
(To find the correct port settings that should be used with your mobile phone or GSM/GPRS modem, one way is to consult the manual of your mobile phone or GSM/GPRS modem. Another way is to check the port settings used by the wireless modem driver that you installed earlier.
To check the port settings used by the wireless modem driver on Windows 98, follow these steps:
a. Go to Control Panel -> Modem.
b. Select your mobile phone or GSM/GPRS modem in the list box.
c. Click the Properties button.
d. The Properties dialog box appears. The Maximum speeds field on the General tab corresponds to HyperTerminal's Bits per second field. Click the Connection tab and you can find the settings for data bits, parity and stop bits. Click the Advanced button and you can find the setting for flow control.
To check the port settings used by the wireless modem driver on Windows 2000 and Windows XP, follow these steps:
a. Go to Control Panel -> Phone and Modem Options -> Modems tab.
b. Select your mobile phone or GSM/GPRS modem in the list box.
c. Click the Properties button.
d. The Properties dialog box appears. Click the Advanced tab and then click the Change Default Preferences button.
e. The Change Default Preferences dialog box appears. The Port speed field on the General tab corresponds to HyperTerminal's Bits per second field. You can also find the setting for flow control on the General tab. On the Advanced tab, you can find the settings for data bits, parity and stop bits.)
|
Figure 7. The screenshot of MS HyperTerminal's Properties dialog box in Windows 98. |
|
|
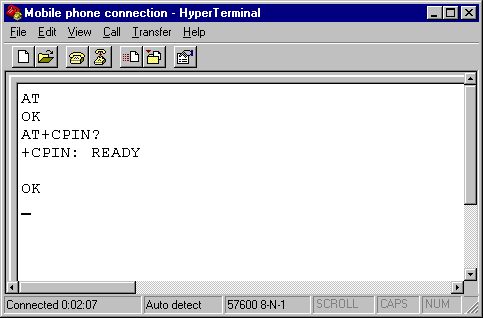
Type "AT" in the main window. A response "OK" should be returned from the mobile phone or GSM/GPRS modem.
Type "AT+CPIN?" in the main window. The AT command "AT+CPIN?" is used to query whether the mobile phone or GSM/GPRS modem is waiting for a PIN (personal identification number, i.e. password). If the response is "+CPIN: READY", it means the SIM card does not require a PIN and it is ready for use. If your SIM card requires a PIN, you need to set the PIN with the AT command "AT+CPIN=<PIN>".
|
Figure 8. The screenshot of MS HyperTerminal's main window in Windows 98. |
|
|
If you get the responses above, your mobile phone or GSM/GPRS modem is working properly. You can start typing your own AT commands to control the mobile phone or GSM/GPRS modem.
Further details about how to use AT commands to send and receive SMS messages will be provided in the following sections.
| Previous Page | Page 19 of 65 | Next Page |
- 1. Introduction to SMS Messaging
- 2. What Makes SMS Messaging So Successful Worldwide?
- 3. Example Applications of SMS Messaging
- 4. What is an SMS Center / SMSC?
- 5. Basic Concepts of SMS Technology
- 6. Intra-operator SMS Messages
- 7. Inter-operator SMS Messages
- 8. International SMS Messages
- 9. What is an SMS Gateway?
- 10. How to Send SMS Messages from a Computer / PC?
- 11. How to Receive SMS Messages Using a Computer / PC?
- 12. Introduction to GSM / GPRS Wireless Modems
- 13. How to Use Microsoft HyperTerminal to Send AT Commands to a Mobile Phone or GSM/GPRS Modem?
- 14. Introduction to AT Commands
- 15. General Syntax of Extended AT Commands
- 16. Result Codes of AT Commands
- 17. AT Command Operations: Test, Set, Read and Execution
- 18. Testing the Communication between the PC and GSM/GPRS Modem or Mobile Phone
- 19. Checking if the GSM/GPRS Modem or Mobile Phone Supports the Use of AT Commands to Send, Receive and Read SMS Messages
- 20. Operating Mode: SMS Text Mode and SMS PDU Mode
- 21. Setting or Reading the Service Center Address / SMSC Address (AT+CSCA)
- 22. Preferred Message Storage (AT+CPMS)
- 23. Writing SMS Messages to Memory / Message Storage (AT+CMGW)
- 24. Deleting SMS Messages from Message Storage (AT+CMGD)
- 25. Sending SMS Messages from a Computer / PC Using AT Commands (AT+CMGS, AT+CMSS)
- 26. Reading SMS Messages from a Message Storage Area Using AT Commands (AT+CMGR, AT+CMGL)
- 27. Appendix A: How to Choose an SMS Service Provider (SMS Gateway Provider, SMS Reseller, SMS Broker)?
- 28. Appendix B: Comparison Table of SMS Service Providers (SMS Gateway Providers, SMS Resellers, SMS Brokers)
- 29. Appendix C: Free Software/Tools and Libraries for Sending and Receiving SMS Messages with a Computer / PC
- 30. Appendix D: GSM 7-bit Default Alphabet Table (with Character Codes of ISO 8859 Latin 1)